
| PMC full text: | J Nutr Biochem. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 Jan 1. Published in final edited form as: J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Jan; 24(1): 353–359. Published online 2012 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.07.005 |
Fig 3
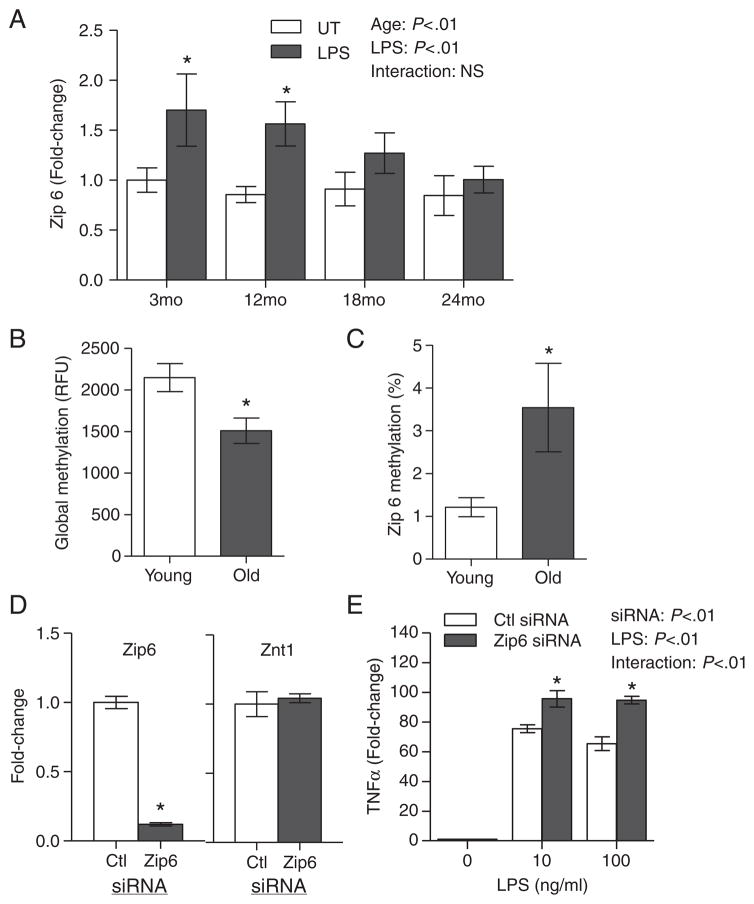
Age-related increase in proinflammatory response was associated with dysregulation of Zip 6 zinc transporter mRNA expression. (A) Changes in Zip 6 expression were determined by real-time PCR in the splenocytes of mice at various ages (n=4 per age group) after stimulation with 1 μg/ml LPS for 6 h, or left untreated (UT). Data represent mean normalized fold-change±S.E.M. vs. UT control. (B) Global DNA methylation status in young (2 months) and aged (26 months) mice (n=11 per age group) was determined. Genomic DNA was isolated from the spleens from each group and analyzed for global DNA methylation changes. Data represent mean RFUs±S.E.M. per 100 ng DNA. *P<.05 vs. young. (C) Zip 6-specific promoter methylation in young (2 months) and aged (26 months) mice (n=15 per age group) was determined using Zip 6-specific EpiTect Methyl Profiler qPCR assay. Data represent percent DNA methylation compared to young mice. *P<.05 vs. young. (D) BMMs were transfected with Zip 6-specific siRNA or control siRNA (n=4 per transfection). Zip 6 and ZnT 1 gene expressions were determined by real-time PCR 24 h post-transfection. Data represent mean normalized fold-change±S.E.M. vs. ctl siRNA. *P<.05 vs. ctl siRNA. (E) siRNA-transfected BMMs were left untreated, or stimulated with 10 or 100 ng/ml LPS for 6 h, and TNFα expression was determined by real-time PCR (n=4). Data represent mean normalized fold-change±S.E.M. vs. ctl siRNA. *P<.05 vs. ctl siRNA. NS, not significant.