| PMC full text: | Published online 2018 Jan 16. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010268
|
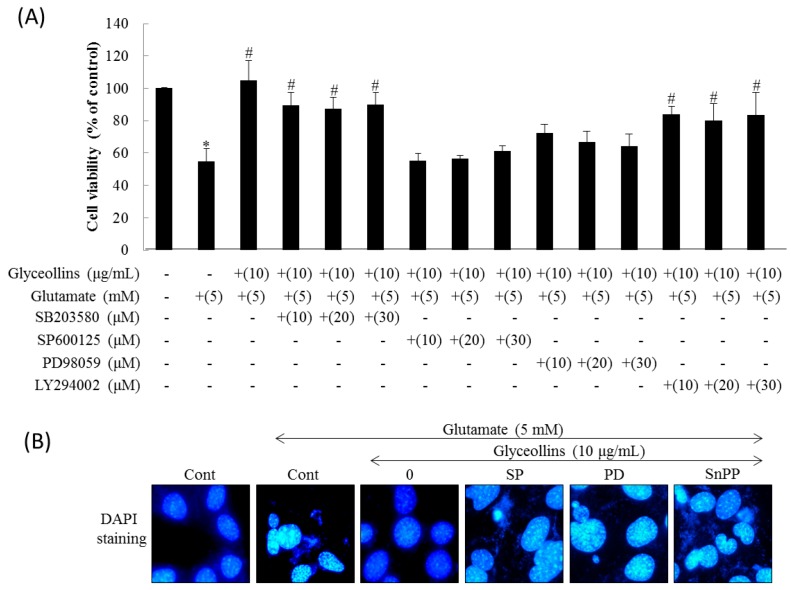
Figure 2
Effects of inhibitors for MAPK, PI3K, and HO-1 on the attenuation of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity by glyceollins. Mouse hippocampal HT22 cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 103 cells/well into 96-well plate and 3 × 104 cells/well into the gelatin-coated 24-well plate for assessment of morphology or DAPI staining, respectively. (A) HT22 cells were treated with MAPK or PI3K inhibitors in the presence of glyceollins (10 μg/mL) and glutamate (5 mM) for 24 h, followed assessing cell viability by MTT assay. Bars represent mean ± SD (n = 4). Marks above each bar indicated the significant difference. *, Significantly different from the untreated control (p < 0.05). #, Significantly different from the positive control group treated with glutamate alone (p < 0.05); (B) HT22 cells were treated with ERK inhibitor (SP), JNK inhibitor (PD), or HO-1 inhibitor (SnPP) in the presence of glyceollins (10 μg/mL) and glutamate (5 mM) for 24 h, followed by DAPI staining and visualizing under fluorescent microscope to evaluate cytotoxicity (magnification, 400×).